Bilateral Salpingectomy Pregnancy
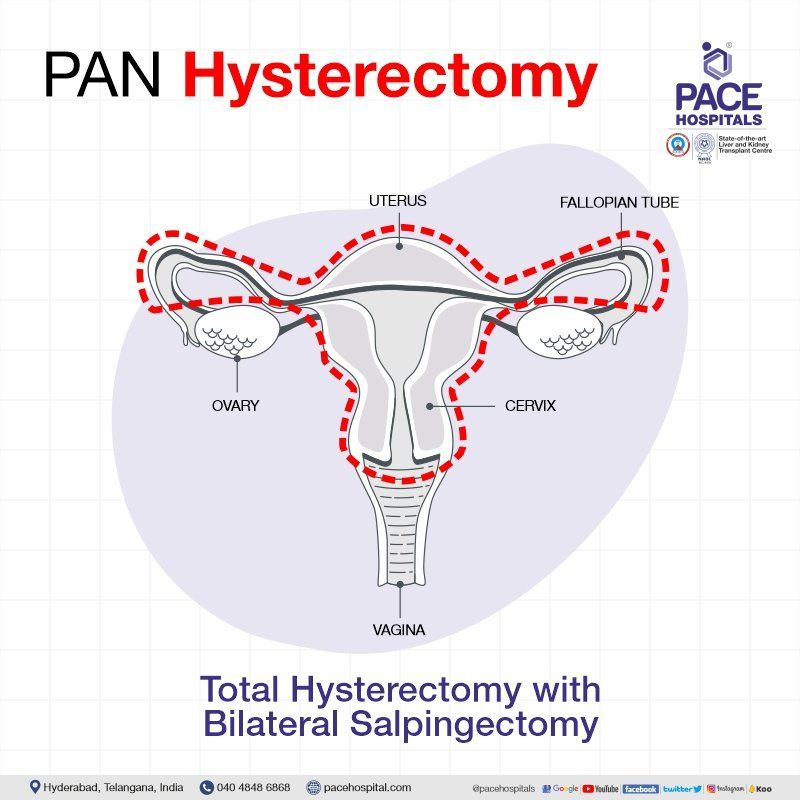
A bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy arises from a fertilized egg implanting outside the uterus, leading to an ectopic pregnancy. Its name derives from the surgical procedure "bilateral salpingectomy" where both fallopian tubes are removed.
Such occurrences are extremely rare, with only a handful of reported cases worldwide. The condition poses significant risks to the mother, emphasizing the relevance of understanding its causes and implications. Advances in reproductive medicine, including the development of laparoscopic techniques, have improved outcomes for patients with this condition.
This article explores the complexities of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy, addressing its diagnosis, risk factors, management approaches, and the ongoing research that aims to prevent and effectively treat this rare but challenging condition.
Read also:Miss Bebesota Nude Unveiling The Truth Behind The Controversy
Bilateral Salpingectomy Pregnancy
Understanding the essential aspects of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy is crucial for effective diagnosis, management, and prevention. These aspects encompass various dimensions, including:
- Etiology: Causes and risk factors
- Pathophysiology: Mechanisms and processes
- Diagnosis: Clinical presentation and diagnostic tools
- Management: Treatment options and strategies
- Prognosis: Expected outcomes and long-term effects
- Prevention: Strategies to minimize risks
- Research: Ongoing studies and advancements
- Psychological impact: Emotional and mental implications
These aspects are intricately connected, shaping the overall understanding and management of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy. They provide a holistic perspective, enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and offer optimal care to patients.
Etiology
Understanding the causes and risk factors of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy is paramount for developing preventive strategies and optimizing treatment approaches. Various factors contribute to the occurrence of this rare condition, ranging from anatomical alterations to hormonal imbalances and genetic predispositions.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Inflammation of the reproductive organs, often caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs), can lead to scarring and blockages in the fallopian tubes. - Endometriosis
Presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, which can cause inflammation and scarring, potentially obstructing the fallopian tubes. - Prior ectopic pregnancy
Women with a history of ectopic pregnancy are at an increased risk of subsequent ectopic pregnancies, including bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy. - Tubal ligation
Surgical sterilization procedure that involves blocking or cutting the fallopian tubes can rarely fail, leading to unintended pregnancy and potentially increasing the risk of ectopic implantation.
These factors highlight the intricate interplay between anatomical, physiological, and surgical interventions that can contribute to the development of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy. A thorough understanding of these causes and risk factors guides preventive counseling, early diagnosis, and appropriate management strategies.
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy involves a complex interplay of mechanisms and processes that deviate from normal reproductive events. Understanding these mechanisms is critical for unraveling the intricacies of this rare condition, guiding clinical practice, and optimizing patient outcomes.
In bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy, the absence of fallopian tubes, typically removed during a bilateral salpingectomy procedure, disrupts the normal path of fertilization and embryo implantation. Despite the absence of fallopian tubes, pregnancy can occur through various mechanisms, including:
Read also:Hey Im Bee Nude The Untold Story Behind The Buzz
- Heterotopic pregnancy: In rare cases, fertilization occurs outside the fallopian tubes, and the embryo implants in the remaining reproductive structures, such as the cervix or ovary.
- Transperitoneal migration: After fertilization in the ovary, the embryo travels through the peritoneal cavity and implants in the pelvic organs, including the abdominal wall or intestines.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF): Assisted reproductive techniques, such as IVF, involve embryo implantation directly into the uterus, bypassing the fallopian tubes.
These mechanisms highlight the intricate adaptations that can occur in the reproductive system, even after surgical interventions like bilateral salpingectomy. Understanding the pathophysiology of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy enables clinicians to make informed decisions regarding fertility counseling, contraception, and management strategies, ensuring optimal care for patients.
Diagnosis
In the context of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy, accurate and timely diagnosis is crucial for ensuring optimal patient outcomes. Given the rarity of this condition and its potential severity, a combination of clinical presentation and diagnostic tools is essential for effective management.
- Symptoms and signs
Patients with bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy may present with various symptoms, including abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and urinary symptoms. These symptoms can mimic other conditions, making diagnosis challenging.
- Physical examination
A thorough physical examination can provide valuable clues, such as abdominal tenderness or adnexal masses, which may indicate an ectopic pregnancy.
- Transvaginal ultrasound
This imaging technique is commonly used to visualize the pelvic organs and detect an ectopic pregnancy. It can help identify gestational sacs and fetal heart activity outside the uterus.
- Serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels
Measuring hCG levels in the blood can help confirm pregnancy and assess its progression. However, it may not be as reliable in bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy due to altered hormone production.
Combining these diagnostic approaches allows clinicians to increase their suspicion for bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy and differentiate it from other conditions. Early and accurate diagnosis is paramount for timely intervention and appropriate treatment, improving pregnancy outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
Management
In the context of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy, effective management hinges on the timely implementation of appropriate treatment options and strategies. The absence of fallopian tubes, a defining characteristic of this condition, necessitates a tailored approach to pregnancy management.
The primary goal of treatment is to terminate the ectopic pregnancy while preserving the patient's reproductive health. This typically involves administering methotrexate, a medication that halts cell growth, or performing a surgical procedure to remove the pregnancy tissue. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the patient's overall health, the location of the pregnancy, and the stage of gestation.
In cases where methotrexate is ineffective or contraindicated, surgery becomes necessary. Laparoscopic surgery, which involves making small incisions in the abdomen, is the preferred approach for bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy. This minimally invasive technique allows for precise removal of the ectopic pregnancy while minimizing the risk of damage to surrounding structures.
Understanding the management options and strategies for bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy is crucial for healthcare professionals and patients alike. Early intervention and appropriate treatment significantly improve pregnancy outcomes, preserve reproductive potential, and prevent life-threatening complications.
Prognosis
In the context of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy, understanding the prognosis, expected outcomes, and long-term effects is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. This knowledge guides decision-making, establishes realistic expectations, and outlines the potential implications of this rare condition.
Bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy poses unique challenges and may have implications for future pregnancies. Since the fallopian tubes have been removed, natural conception is no longer possible. Therefore, patients who desire future pregnancies may consider options such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) with the transfer of embryos into the uterus.
Long-term effects of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy may include an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy in a remaining reproductive structure, such as the cervix or ovary. Regular follow-up and monitoring are essential to detect and manage any potential complications.
Understanding the prognosis of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy allows patients and clinicians to make informed choices about treatment options, reproductive planning, and long-term care. By considering the potential outcomes and effects, patients can proactively address their health concerns and make decisions that align with their goals and well-being.
Prevention
In the context of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy, understanding preventive strategies to minimize risks is of paramount importance. Given the rarity and potential severity of this condition, proactive measures to reduce the likelihood of its occurrence are essential for improving women's health outcomes.
One critical component of prevention involves mitigating risk factors associated with bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy. This includes promoting awareness about pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and endometriosis, as well as encouraging prompt diagnosis and treatment of these conditions to minimize the risk of tubal damage and scarring.
Furthermore, counseling women who have undergone tubal ligation or bilateral salpingectomy about the small but potential risk of pregnancy is crucial. In such cases, regular monitoring and early detection of any symptoms suggestive of pregnancy are essential to ensure timely intervention and appropriate management.
By implementing these preventive strategies, healthcare providers can play a significant role in minimizing the incidence of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy. This not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces the emotional and physical toll associated with this rare condition.
Research
Research plays a critical role in understanding and addressing the complexities of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy. Ongoing studies and advancements aim to shed light on the causes, risk factors, and potential preventive measures for this rare condition.
One area of research focuses on identifying the underlying mechanisms that contribute to bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy. By studying the molecular and cellular processes involved, researchers aim to develop targeted therapies or interventions that can prevent or treat this condition. Additionally, ongoing studies explore the long-term effects of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy on women's reproductive health and overall well-being.
Real-life examples of research advancements include the development of minimally invasive surgical techniques for managing bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy. Laparoscopic surgery, which involves making small incisions in the abdomen, has become the preferred approach due to its precision and reduced risk of complications. Furthermore, advancements in fertility preservation techniques offer hope to women who desire future pregnancies after undergoing bilateral salpingectomy.
The practical applications of understanding bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy extend beyond clinical management. Research findings contribute to the development of evidence-based guidelines and educational resources for healthcare providers and patients. By raising awareness and promoting early detection, research helps reduce the incidence of complications and improves overall outcomes.
Psychological impact
Bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy, a rare condition where pregnancy occurs outside the uterus despite the absence of fallopian tubes, poses unique emotional and mental challenges for individuals. The psychological impact of this condition stems from the complex interplay of physical, hormonal, and social factors.
The unexpected nature of pregnancy after bilateral salpingectomy can trigger feelings of shock, disbelief, and anxiety. Individuals may grapple with grief over the loss of their fallopian tubes and the implications for future fertility. Hormonal changes associated with pregnancy can further intensify these emotions, leading to mood swings, irritability, and depression.
Real-life examples of the psychological impact of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy include:
- A woman who underwent bilateral salpingectomy for sterilization purposes experiencing intense feelings of guilt and self-blame upon discovering an ectopic pregnancy.
- A couple who had been trying to conceive for several years experiencing emotional turmoil and relationship strain after learning that pregnancy occurred outside the uterus, despite the woman's bilateral salpingectomy.
Understanding the psychological impact of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy is crucial for healthcare providers. It enables them to provide comprehensive care that addresses not only the physical aspects of the condition but also the emotional and mental well-being of patients. This may involve providing emotional support, offering counseling services, and connecting individuals with support groups or online communities.
In conclusion, bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy, though rare, presents unique challenges and complexities that require a multifaceted understanding. This article has explored the various aspects of this condition, encompassing its causes, diagnosis, management, prognosis, prevention, ongoing research, and psychological impact. Key points highlighted throughout the article include the importance of recognizing risk factors, implementing preventive strategies, and employing minimally invasive surgical techniques for management. Furthermore, the emotional and mental implications of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy demand attention and support from healthcare providers.
As our understanding of this condition continues to evolve through ongoing research, it is imperative to maintain awareness and promote evidence-based practices. By fostering collaboration between healthcare professionals, researchers, and individuals affected by bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy, we can strive to improve outcomes, reduce complications, and provide holistic care that encompasses both physical and emotional well-being. Ultimately, a deeper understanding of bilateral salpingectomy pregnancy empowers us to support and empower individuals in their reproductive journeys, even in the face of unexpected challenges.